In today's interconnected world, where data breaches and privacy concerns continue to make headlines, ensuring the security of our online communication has become more critical than ever. Email, one of the most widely used communication channels, has been a primary target for hackers and cybercriminals.
To address these concerns, modern encryption protocols have emerged to provide robust security for email communications. In this article, we will explore eight of these encryption protocols and how they shape the changing face of email security. You can seek professional IT services for added protection and network support.
8 Modern Encryption Protocols for Email Security
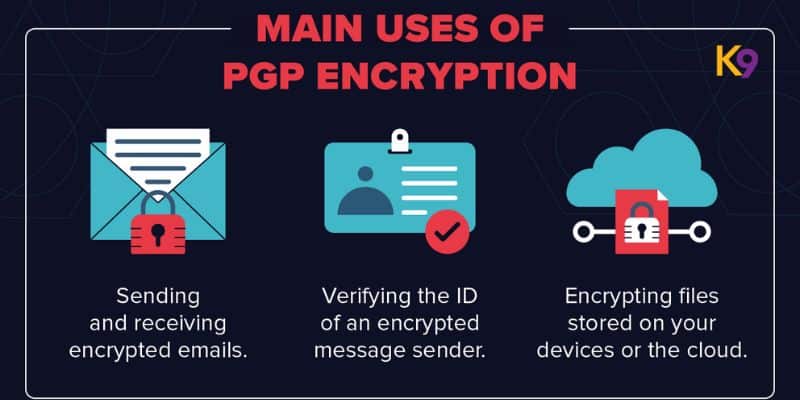
1. Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)
One of the first and most popular encryption methods for email security is Pretty Good Privacy or PGP. In PGP, symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods are combined in a hybrid encryption scheme. The message content is encrypted using public-key cryptography, ensuring only the intended receiver can decrypt and read it. PGP has established itself as robust and trustworthy, and its open-source status has cultivated a community-driven security philosophy.
2. Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME)
S/MIME is another widely adopted encryption protocol for email security. It provides end-to-end encryption by leveraging digital certificates from trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). S/MIME integrates seamlessly with email clients, enabling users to digitally sign and encrypt their messages. The digital signatures verify the sender's authenticity, while encryption protects the content from unauthorized access.
3. Transport Layer Security (TLS)
TLS is crucial in email security, although it is generally used to secure web communications. TLS guarantees an encrypted and secure connection between email servers, protecting the transfer of emails while they are in transit. When two email servers implement TLS, they create a secure channel and encrypt the information sent back and forth. This protocol is essential for preventing email traffic eavesdropping and tampering.
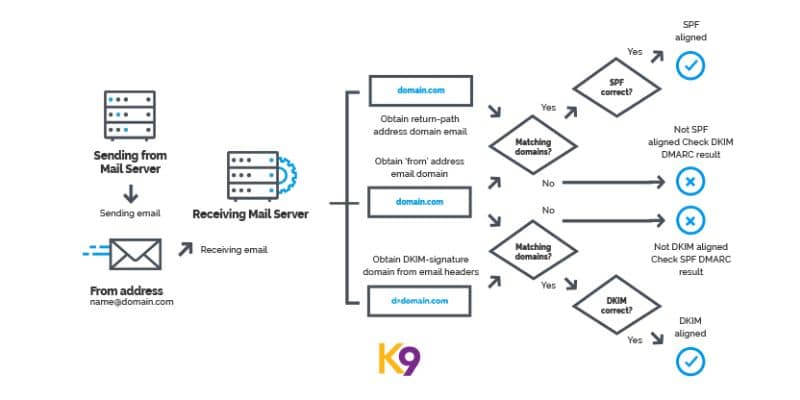
4. DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)
DKIM is an algorithm for email authentication that focuses on confirming the sender's legitimacy and identifying email manipulation. Outgoing communications now include a digital signature that enables receivers to verify the legitimacy and origin of the email. The email headers are signed by DKIM using public-key cryptography, confirming that they haven't been changed in transit. This protocol improves email security and helps prevent phishing attempts.
5. OpenPGP
OpenPGP is an open standard that builds upon the PGP encryption protocol. It offers a high level of security for email communications by providing end-to-end encryption and digital signatures. OpenPGP has gained popularity due to its interoperability and compatibility with various email clients and operating systems. It allows users to securely exchange encrypted messages across different platforms and ensures email content's confidentiality and integrity.
6. Domain-Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC)
DMARC is a protocol that complements DKIM and SPF (Sender Policy Framework) to provide email authentication and prevent email spoofing. DMARC allows domain owners to specify policies for how receiving email servers should handle emails from their domain. It helps reduce phishing and spam by providing mechanisms to verify the alignment between the sender's domain and the email's header information.
7. STARTTLS
Email communications can benefit from an opportunistic encryption technique thanks to STARTTLS, an enhancement of the SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol). The email transmission can be encrypted when two email servers implement STARTTLS and establish a secure TLS connection. However, it's crucial to remember that STARTTLS is vulnerable to downgrade attacks and depends on both email servers supporting the protocol for reliable encryption.
8. Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
While SSL is frequently linked with protecting web traffic, it also has uses in email security. Sensitive information, such as login and email content, can be safeguarded using SSL to encrypt the connection between the email client and the server. Users can confidently communicate, knowing they are interacting with a dedicated server and not a hostile entity, thanks to SSL certificates provided by reputable CAs that confirm the legitimacy of the email server. Using SSL improves email security, reducing the possibility of illegal access and data interception.
As the email security landscape evolves, these modern encryption protocols are at the forefront of protecting sensitive data and ensuring secure communication channels.
However, it's worth noting that the effectiveness of encryption protocols also depends on proper implementation and adherence to best practices. It is essential for organizations and individuals to stay updated with the latest advancements in email security and regularly update their systems to mitigate emerging threats.
Moreover, while encryption protocols are vital in securing email communications, adopting a holistic approach to email security is crucial. This includes employing strong and unique passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, being cautious of phishing attempts, and regularly updating and patching software and email clients to address vulnerabilities.
Why You Should Invest in Email Security
Here are some reasons you should hire the best IT management team to secure your incoming and outgoing emails:
1. Sensitive Information Protection:
Sensitive and confidential information like financial data, personal details, trade secrets, and intellectual property are frequently transmitted by email. By investing in email security measures like encryption techniques, you can ensure that this important data is kept secure and out of the hands of unauthorized people. Protect the confidentiality and integrity of important data by protecting your email communications.
2. Mitigation of Data Breach Risks:
Data breaches can have severe consequences for individuals and organizations, including financial loss, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Cybercriminals often target email accounts to gain access to sensitive data, which can then be used for identity theft, fraud, or sold on the dark web. By investing in robust email security solutions, you can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches, protecting your personal and business information.
3. Prevention of Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks:
Phishing attacks, where cybercriminals impersonate trustworthy entities to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious attachments, are a prevalent threat in the digital world. Investing in email security tools and technologies can help identify and block phishing emails, preventing employees and individuals from falling victim to these deceptive tactics. You can significantly reduce the risk of phishing attacks by implementing email filtering, anti-spam solutions, and real-time threat detection.
4. Protection of Business Reputation:
A company's reputation can be badly harmed by a security breach or a compromised email account. It can undermine consumer trust, lead to missed business opportunities and damage a brand's reputation. By proactively investing in email security, you show that you are dedicated to safeguarding private information and upholding a safe working environment. As a result, your business's reputation in the industry is maintained, relationships are strengthened, and client confidence is increased.
Conclusion
In conclusion, as cyber threats continue to evolve, the need for robust email security becomes paramount. The modern encryption protocols discussed in this article offer effective solutions to protect our email communications from unauthorized access and tampering. By leveraging these protocols, individuals and organizations can enhance their privacy and maintain the confidentiality of their sensitive information in an increasingly interconnected digital world.



You must be logged in to post a comment.